|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Try this core stability workout to improve mobility, stabilize your core and lean out your body!
@ptahuntsville Core stability drills 💪🏼 #core #corestrength #fitnesstips #physicaltherapy #rehab #huntsvilletexas #huntsville #texas #fitness #orthopedic #health #healthylifestyle #goals #agility #speed #power #performance #sportsmedicine #sportsmed #shsu #athlete #cupping
As another March Madness tournament comes to a close, legions of college basketball fans are in pain, mourning their unrealized title hopes as if they’d just lost a loved one. For some, the emotional pain is nearly unbearable – bordering on the physical. A busted bracket can hurt as bad as a busted knee, it seems. But this only seems true for those of us with healthy knees. As all who suffer from knee pain know all too well, the “madness” to which college basketball fans are so often driven to in March pales in comparison to the “madness” of knee pain when, for example, it stops you from fully enjoying an afternoon of particularly beautiful weather, or the company of friends or family without consistently wincing in pain. This is a reality for many, as one in four adults currently suffer from some form of knee pain – a figure that’s increased nearly 65% over the last twenty years – according to a 2018 paper published in the AFP (American Family Physician) medical journal. Due to the sheer prevalence of knee pain, it’s wise to familiarize yourself with the common causes, treatments and prevention tips in order to be adequately prepared. In this article, we will lay out the common types and causes of knee pain, as well as general prevention and recovery tips, from the view of a physical therapist.
“Knee pain” is an extremely wide-ranging category. It not only includes a large number of possible symptoms – all of which vary both in terms of their severity and their particular placement within the anatomy of the knee – but also a vast range of potential victims. That being said, a brief overview of “the basics” might be helpful. First, it’s important to understand the vital role that the knee places in terms of our anatomy and mobility. The knee is a large weight-bearing joint, that is comprised of three cartilage-layered bones, which acts as a central connection point for various ligaments, tendons, muscles and connective tissue. These various components work in conjunction with each other to allow us to perform simple mobility tasks, like standing, walking, or running. That being said, it’s easy to see why any pain within the knee can be so disruptive to our everyday lives.
Generally speaking, all causes of knee pain fall into one of four basic categories of underlying causes – aging, injury, overuse, or other medical conditions. Specific conditions can be roughly associated with certain categories. For example, various forms of arthritis can usually be associated with aging, whereas patella tendinitis might be generally associated with overuse. Arthritis and tendinitis account for a large majority of knee pain, and though certainly painful, they are generally less serious than knee pain resulting from either injury or special medical conditions. They are usually accompanied by chronic (dull, aching, cumulative) pain, as opposed to acute (sharp, piercing, immediate) pains that can be indicative of serious injuries. It follows that if your pain is of the acute nature – particularly if and when combined with other symptoms, such as a complete inability to bear weight – that it might be wise to seek immediate medical consultation.
If this is the case for you, by all means seek immediate medical attention (PTA offers free consultations for situations just like this one, in fact). The unfortunate reality of most “serious” knee injuries is that, in best cases, they will likely require regular physical therapy treatment in order to properly heal, and in worst cases, surgery might prove unavoidable. In addition, because these injuries often happen so fast – literally in seconds, or less than that – and because they are so often caused by nothing more than bad luck, the tragedy that at times arises from pure chance, there’s not much to be done in terms of prevention. What you can do, however, is make a conscious point to protect your own body if you’re partaking in any physical activity where you feel that your body might be potentially be at risk, as well as consistently and thoroughly stretching beforehand. In addition, there is one skill which you can practice, unlike our first two prevention tips, and that is your level or ability (or lack thereof) to balance. An interesting note is that knee pain can cause balance difficulty (which can lead to other injuries) and balance deficits can cause knee injury from falls. If you happen to suffer one of the more common causes of knee pain, such as arthritis, a wider range of preventative tools are at your disposal. These include, among others, avoiding high-impact activities, maintaining a healthy weight, keeping body inflammation levels low, and wearing supportive shoes as well as regularly replacing them. Please feel free to drop by any of our multiple PTA locations in either Conroe, or Huntsville, Texas, for a free consultation today! Your recovery might be closer than you think.
Written by Clay Williams
Reviewed by Dallas Williams, PT and Owner of Physical Therapy Associates
Sources:
Bunt, Christopher, et al. “Knee Pain in Adults and Adolescents: The Initial Evaluation.” American Family Physician, 1 Nov. 2018, https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2018/1101/p576.html.
“Knee Pain.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 25 Jan. 2023, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20350849.

In 2018, on another routine work day as a maintenance director for Walker County facilities, Marvin Cannon was on the roof of one of his precinct buildings, overseeing a repair, when he stepped through a pane of transparent fiberglass that had blended in with the roof, and continued to fall twenty-five feet to the concrete building floor. Or this is what he is told. As Mr. Cannon recalls, the moment he realized he was falling – he lost consciousness. When he awoke, his life had drastically changed: though somehow no bones had been broken below his waist, there was severe damage to the right side of his body – including a nearly shattered elbow that continues to cause problems today – not to mention a number of vertebrae that had been battered in the fall, resulting in Mr. Cannon’s need for a wheelchair. A wheelchair which most of his eleven doctors warned him that he might have to get used to – permanently.
This is the groundwork that had been laid for Mr. Cannon – mentally – when he first arrived at Physical Therapy Associates. It’s almost no wonder that, as Mr. Cannon openly admits, he had “absolutely no confidence” that he would ever walk again that first day. Anyone who has suffered from such a massive injury before – or anyone who has witnessed first-hand its detrimental effects on others – can attest to this, to the sense of complete deflation that can sometimes overwhelm individuals in the beginning stages of treatment. Full rehabilitation can seem like a distant fairy tale, especially to someone in a wheelchair.
But over the course of his treatment, we were able to help instill the necessary self-confidence in Mr. Cannon, and, suddenly, things began to change. As Mr. Cannon says: “Once I got it in my mind that I wanted to do it, and when I realized that I could do it – everything turned around.” “Everything turned around” to the point that, if you were to meet the man today, it would seem unimaginable that he could be so recently involved in such a traumatic accident. After suffering major spinal injuries – and after hearing doctor after doctor warn him again and again of a lifetime of paralysis – Mr. Cannon walks taller today than he ever has.
That’s not to say that the road has been easy, or that Mr. Cannon does not still face pains as a result of his injury on a daily basis. But this matters little to Mr. Cannon in scope of what he’s had to endure. And you can hear it in his voice – the pure joy, a renewed gratitude for living, even. As Mr. Cannon will tell you, life – every day – is a gift, and a fragile one too. For most of us, especially the younger crowd, it’s commonplace to coast through day-to-day life unaware of this fact, fully-occupied by the daily hustle and bustle of errands, responsibilities, dinner parties, completely oblivious to the grim reality that it could all change so quickly. Mr. Cannon’s story is a testament to this grim reality, but, more importantly, it’s a testament to the rebirth, the sense of new life, that can grow out of these darker, more painful moments of our lives. Mr. Cannon even goes so far as to call it just that – “it’s a new life,” he says, and it’s one he is certainly enjoying.
At Physical Therapy Associates, we realize that the task of recovery can seem daunting, impossible, even, as it first appeared to Mr. Cannon that first day he rolled his wheelchair – or his “turtle shell,” as he calls it – into our facilities. But over time, with resiliency, the right habits, and with us cheering you on in your corner, we believe that the “impossible” becomes manageable.
Today, despite “having more hardware than Ace Hardware,” Mr. Cannon soaks up every second he can with his wife and his family, and gives all glory to God whenever given the chance.
Author Clay Williams
Tiger Woods has not played in an official golf tournament since the Masters in 2020. On April 7th he once again took up his clubs in pursuit of another green jacket.
The past year and a half has not necessarily been a walk in the park for the recent Hall of Fame inductee. In December 2020 he underwent another back surgery and then in February 2021 he was in a very serious car accident. Woods suffered open fractures in his R leg, as well as injuries to his ankle and foot which required internal fixation – pins and screws.
However, Woods is no stranger to surgeries and subsequent rehab. As a long-term athlete, wear and tear are your constant companions. Over the course of his career he has had 5 back surgeries as well as 5 left knee surgeries. In May of 2021 Golf Digest published an article on Woods’ physical therapy. In the article, he described his therapy as ‘more painful than anything I have ever experienced.’ For a while, he stated, his number one goal was being able to walk on his own again.
As I watched him walk out onto the range in Augusta I couldn’t help but ask – What makes his outcome different from other individuals? What steps did he take that have allowed him to return to the Master’s? What can you or I take away from his come back that may help us persevere?
1. Physical Condition Did Tiger Woods’ athleticism contribute to his post surgical outcomes? Could my come back be better if I was in better shape before hand? Yes. Being in better shape will help you rebound faster after injury and/or surgery. In fact, getting ‘into shape’ may also stave off surgery for those aches and pains that keep you from your full activities. Talk to your doctor about an exercise program that may help you get back to tip top condition. By the way… PT can help with this too.
2. Consistency Woods noted in his Golf Digest interview that he did his routine EVERY DAY. While we all have activities that keep us busy every day, could we spare just a few minutes to pour our energy into getting our body moving properly and getting stronger? Is your body important enough to you? I would encourage you to make your body a priority. Jobs, hobbies and companions may come and go, but you only have one body per lifetime.
3. Positivity Scrolling through Instagram and golfing sites you don’t find Woods lamenting his condition. He is not speculating on his future prospects – what he might or might not be capable of in the future. He’s not making excuses for his activities. Instead, he focuses on how he is progressing and will continue to work harder. I do not know Woods, but I know that a person’s thoughts have power and Woods’ public conversations show that he’s not going to let negative comments from his own mouth limit his future. Henry Ford said it best, ‘whether you think you can or think you cannot, you are right.”
Written by Christa Ikard, PT, DPT
What is it?
The American Physical Therapy Association describes dry needling as a ‘skilled intervention that uses a thin filiform needle (an acupuncture needle) to penetrate the skin and stimulate underlying myofascial trigger points, muscular and connective tissues for the management of neuromusculoskeletal pain and movement impairments.
What that means is that dry needling is used to treat trigger points, muscle tension, and scar tissue in muscles, lining of muscles and connective tissues. We also use dry needling to change the basic elements that your body perceives as painful. The overall goal of dry needling is to improve how your body functions at the most basic level – muscles, nerve and the tissues that connect them all – so that you can be more active.
What conditions can be treated by it.
Common conditions that may benefit from dry needling are neck pain, shoulder impingement, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, headaches, TMJ, knee pain, shin splints, plantar fasciitis, and low-back pain. Dry needling adds to the “tools in the tool box” of a physical therapist.
The science behind it.
Treatment for myofascial trigger points: Trigger points are tight bands of tissues in muscles. This causes less circulation in that spot; which means there is less blood supply and oxygen, and a build up of unhealthy chemicals. This toxic environment is not only present in the muscle, but it extends to the nerves that make the muscle work too. When a therapist inserts a needle into the trigger point it activates the nerve which alerts the brain to send helper cells to improve the health in the local tissues around the needle and expedite the healing process.
Treatment for scar tissue, fascia and connective tissue: A Needle is inserted superficially around the areas of adhesions or restrictions. Needle rotation facilitates mechanicotransduction (the processes through which cells sense and respond to mechanical stimuli by converting them to signals that elicit specific cellular responses – in this case tissue relaxation).
Treatment for excessive muscle tension: Research has shown that dry needling activates fibroblasts (a cell in connective tissue which produces collagen and other fibers) through the mechanical manipulation of the needle which releases beneficial chemical and other pro-inflammation mediators.
But wait, isn’t inflammation bad?
Not always!!
Inflammation reactions are your body’s natural way of restoring your functionality and healing itself. This process is known as the inflammatory response. This response occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat or any other cause. The damaged cells release chemicals (including histamine, bradykinin, and prostaglandins) that cause blood vessels to leak fluid into the tissues, causing swelling. This helps isolate the foreign substance from further contact with body tissues. The chemicals also attract white blood cells called phagocytes that “eat” germs and dead or damaged cells. Basically, the therapist manipulates your body into restoring itself by triggering this inflammatory response when they rotate the needle after insertion into these areas of muscle tension.
Who should not have dry needling?
This isn’t for everyone, if fact those who are pregnant, afraid of needles, people taking blood thinners and those recovering from a recent surgery should not undergo this treatment. For the rest of us who need pain or movement restriction reduced, it may be a great option.
For more information, including references, please see: https://www.apta.org/StateIssues/DryNeedling/ClinicalPracticeResourcePaper/

Pregnancy is a beautiful process, but creating human life is far from easy and comes with many complications. Extra hormones and blood flow combined with weight gain and shifts in center of gravity can lead to a variety of issues such as:
Physical therapists can evaluate and treat for prenatal and post natal care, ensuring a smoother pregnancy, labor and delivery process. 50-70% of pregnant women experience back pain, and most view these aches and pains as an unfortunate but unavoidable complication of pregnancy. Staying active greatly reduces pregnancy complications, including back pain, hip pain and postural issues. Physical therapy can help by teaching proper form to stretch and strengthen as well as establishing home exercise programs that patients can feel confident in doing on their own.
Physical Therapy Associates wants to help, we are offering “Mama lunches” every Tuesday at our Conroe location and every Thursday at our Huntsville location. These lunches will provide free lunch and information further detailing the benefits of physical therapy for prenatal and post natal care, as well as allow mom-to-be’s the opportunity to meet the physical therapists and tour the facility before scheduling their evaluation appointments. Call us at our Huntsville office (936-294-0283) or our Conroe office (936-494-1292) to schedule your luncheon.
We are excited to announce that as of September 1st, a doctors prescription will no longer be required to begin physical therapy treatment. We have been eagerly awaiting this legislation to be passed in the state of Texas, where we were one of only two states to still have limited access to patient treatment.
Why is this so exciting? Direct patient access allows YOU to be your own advocate and begin therapy sooner without the hindrance of waiting to be seen by your doctor and spending the money on an office visit copay.
A May 2018 study on patients with low back pain found that patients who saw a physical therapist at the first point of care significantly lowered out of pocket costs and the unnecessary use of other costly services including opioid prescriptions, imaging services, and emergency department visits. Results from another 2018 study on patients with neck pain supported these findings with the authors adding, ” current trends in health care costs are becoming unsustainable for payers and patients and are not resulting in improved outcomes…consulting a physical therapist early may provide an opportunity to mitigate downstream health care utilization while containing costs.”
Out of all the states in the nation, Texas was ranked 47th in access to physicians in 2015. In 2017, patients in Houston were waiting an average of 19 days to access a primary care physician.

This is problematic when you consider that optimal physical therapy outcomes are obtained when treatment is started within the first 3 weeks. With the current laws, you would have spent that time waiting to see your doctor.
Some insurances may still require referrals or prescription based on plan types. If you would like to know more about your insurance or would like to start your treatment do not hesitate to call us!
Together We Can Overcome!
Back to school time can be hectic. Parents frantically trying to buy school supplies, teachers trying to get their rooms ready and kids fighting the inevitability of Summer ending. The new school year is coming whether you are ready or not, but you shouldn’t have to deal with all the stresses that come with it AND back pain too! Here are some helpful stretches that can help reduce pain and keep you going!
Pelvic Tilts:
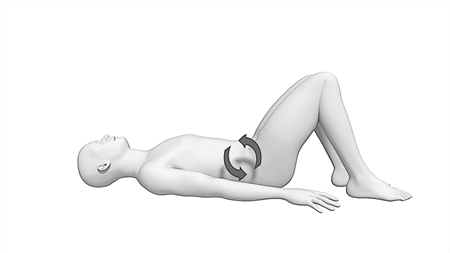
While lying on your back with your knees bent, rotate your hips so that your belly button comes towards you and inwards. Pull in with your abdomen, don’t push with your feet. Repeat 20 times.
Lower Trunk Rotation:
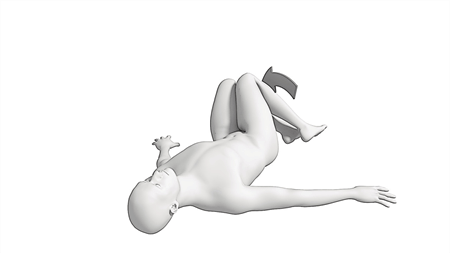
While lying on your back with your knees bent, slowly allow your knees to fall to one side until a stretch is felt. Keep your knees together. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times on both sides.
Prayer Stretch:
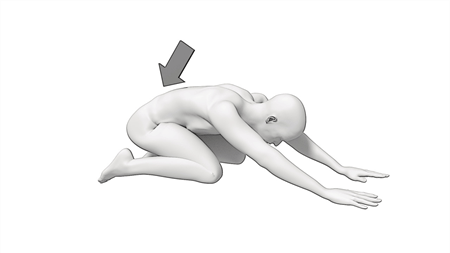
While on your hands and knees, gently sit down towards your feet until a stretch is felt in your lower back. This is the most comfortable on a bed with your feet hanging off the edge. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat three times.
Hip Flexor Stretch:
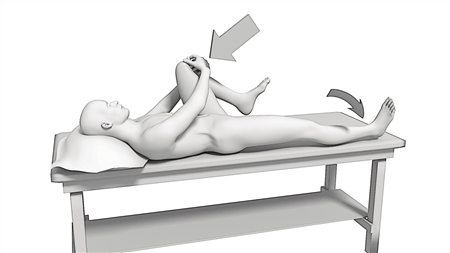
While lying on your back, pull both knees up to your chest to flatten your lower back. Then slowly lower one leg down until a stretch is felt in the front of that hip. Keep one knee to your chest! Hold 30 seconds and repeat 3 times on both sides!
If you have persistent pain or your pain worsens, call Physical Therapy Associates to schedule your evaluation and determine if you’re a good candidate for physical therapy.
Looking for a place to keep yourself active because your living room floor just isn’t cutting it anymore? Look no further than this blog post because we may have the answer. Huntsville has tons of hidden gems just waiting for you to explore and find your exercise niche.
Here are some gyms located in Huntsville along with their websites so you can find out more information about each of them to pick the one that best fits you and your workout needs. They are listed in no order of recommendations since finding the right gym is a personal preference based on goals and needs. The best gym for you is the one you will actually attend consistently.
Lastly, have you ever considered playing in the park as a workout? Well Huntsville is definitely not short on park space and I’m here to tell you that a park can be an excellent resource for exercise! Here are some of my favorite spots in Huntsville to get some fun, dynamic, outdoor workouts: Kate Barr Ross Memorial Park, Eastham-Thomason Park, Thomas Henry (Josey) Ball Park, Sam Houston State’s Intramural fields & the Huntsville State Park ($5/person entry fee). Those are just a few of the great hidden gems in Huntsville that can be turned into your own personal gym space! Give them a try!
Note: Updated 10/8/2022